First in, First out (FIFO) is an inventory model in which the first acquired receipts are issued first. Financially updated issues from inventory are settled against the first financially updated receipts into inventory based on the financial date of the inventory transaction.
When using FIFO, you can choose to mark inventory transactions so that a specific receipt is settled against a specific issue instead of following the FIFO rule.
We recommend a periodic inventory closing when you use the FIFO inventory model.
The following examples illustrate the impact of using FIFO with three different configurations:
-
FIFO without the option
-
FIFO with the option
-
FIFO with marking
 FIFO without
the Include physical value option
FIFO without
the Include physical value option
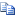
In this FIFO example, the inventory model group is not marked to include physical value.
The following transactions are illustrated in the graphic below:
-
1a. Inventory physical receipt for a quantity of 1 at a cost of USD 10.00 each.
-
1b. Inventory financial receipt for a quantity of 1 at a cost of USD 10.00 each.
-
2a. Inventory physical receipt for a quantity of 1 at a cost of USD 20.00 each.
-
2b. Inventory financial receipt for a quantity of 1 at a cost of USD 20.00 each.
-
3a. Inventory physical receipt for a quantity of 1 at a cost of USD 25.00 each.
-
4a. Inventory physical receipt for a quantity of 1 at a cost of UD 30.00 each.
-
4b. Inventory financial receipt for a quantity of 1 at a cost of USD 30.00 each.
-
5a. Inventory physical issue for a quantity of 1 at cost price of USD 20.00 each (running average of financially updated transactions).
-
5b. Inventory financial issue for a quantity of 1 at cost price of USD 20.00 each (running average of financially updated transactions).
-
6. Inventory close is performed. Based on the FIFO method, the first financially updated issue will be settled to the first financially updated receipt. An adjustment of negative USD 10.00 will be made on the issue transaction.
The new running average cost price reflects the average of the financially updated transactions.
The following diagram illustrates this series of transactions with the effects of choosing the FIFO inventory model without the option.
Key to diagram
-
Inventory transactions are represented by vertical arrows.
-
Receipts into inventory are represented by vertical arrows above the timeline.
-
Issues out of inventory are represented by vertical arrows below the timeline.
-
Above (or below) each vertical arrow, the value of the inventory transaction is specified in the format Quantity@Unit price.
-
An inventory transaction value surrounded by brackets indicates that the inventory transaction is physically posted into inventory.
-
An inventory transaction value without brackets indicates that the inventory transaction is financially posted into inventory.
-
Each new receipt or issue transaction is designated with a new label.
-
Each vertical arrow is labeled with a sequential identifier, such as 1a. The identifiers indicate the sequence of inventory transaction postings in the timeline.
-
Inventory closings are represented by a red vertical dashed line and the label Inventory Close.
-
Settlements that are performed by inventory close are represented by dotted red arrows going diagonally from a receipt to an issue.
 FIFO with the
Include physical value option
FIFO with the
Include physical value option
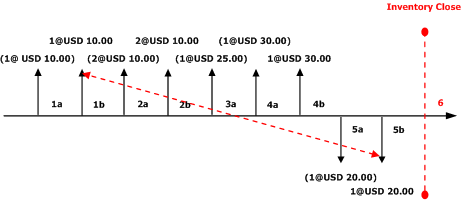
If the box is selected for an item in the form, Microsoft Dynamics AX will use both physical and financial receipt transactions to calculate the running average cost price. Where applicable, the system will also make adjustments to the physically updated issue transaction. When the box is cleared, inventory close with the FIFO inventory model will make settlements only to transactions that are financially updated.
The following transactions are illustrated in the graphic below:
-
1a. Inventory physical receipt for a quantity of 1 at a cost of USD 10.00 each.
-
1b. Inventory financial receipt for a quantity of 1 at a cost of USD 10.00 each.
-
2a. Inventory physical receipt for a quantity of 1 at a cost of USD 20.00 each.
-
2b. Inventory financial receipt for a quantity of 1 at a cost of USD 20.00 each.
-
3a. Inventory physical receipt for a quantity of 1 at a cost of USD 25.00 each.
-
4a. Inventory physical receipt for a quantity of 1 at a cost of USD 30.00 each.
-
4b. Inventory financial receipt for a quantity of 1 at a cost of USD 30.00 each.
-
5a. Inventory physical issue for a quantity of 1 at a cost price of USD 21.25 each (running average of financial and physical updated transactions).
-
5b. Inventory financial issue for a quantity of 1 at a cost price of USD 21.25 each (running average of financial and physical updated transactions).
-
6a. Inventory physical issue for a quantity of 1 at a cost price of USD 21.25 each.
-
7. Inventory close is performed. Based on the FIFO method, the first financial issue transaction will be adjusted or settled to the first updated receipt, either financial or physical.
Transaction 5b will be settled to the receipt transaction 1b. There will be an adjustment of negative USD 11.25 to this issue transaction.
The new running average cost price reflects the average of the financially and physically updated transactions at USD 27.50.
The following diagram illustrates this series of transactions with the effects of choosing the FIFO inventory model with the option.
Key to diagram
-
Inventory transactions are represented by vertical arrows.
-
Receipts into inventory are represented by vertical arrows above the timeline.
-
Issues out of inventory are represented by vertical arrows below the timeline.
-
Above (or below) each vertical arrow, the value of the inventory transaction is specified in the format Quantity@Unit price.
-
An inventory transaction value surrounded by brackets indicates that the inventory transaction is physically posted into inventory.
-
An inventory transaction value without brackets indicates that the inventory transaction is financially posted into inventory.
-
Each new receipt or issue transaction is designated with a new label.
-
Each vertical arrow is labeled with a sequential identifier, such as 1a. The identifiers indicate the sequence of inventory transaction postings in the timeline.
-
Inventory closings are represented by a red vertical dashed line and the label Inventory Close.
-
Settlements that are performed by inventory close are represented by dotted red arrows going diagonally from a receipt to an issue.
 FIFO with
marking
FIFO with
marking
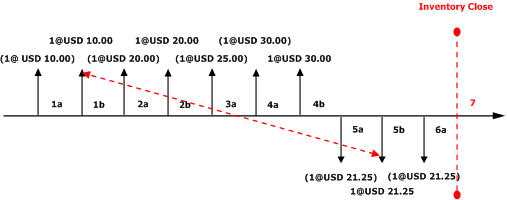
Marking is a process in Microsoft Dynamics AX that allows you to link, or mark, an issue transaction to a receipt transaction. Marking can occur either before or after a transaction is posted. You can use marking when you want to be sure of the exact cost of the inventory when the transaction is posted or when the inventory close is performed.
For example, suppose the Customer Service department accepted a rush order from an important customer. Because this is a rush order, you will have to pay more for this item to accommodate your customer's request. You would like to be certain that the cost of this inventory item is reflected in the margin, or cost of goods sold (COGS) for this sales order invoice.
When the purchase order is posted, the inventory is received at a cost of USD 120.00. If this sales order document is marked to the purchase order before the packing slip or invoice is posted, the COGS will be USD 120.00 instead of the current running average cost for the item. If the sales order packing slip or invoice is posted before the marking occurs, the COGS will be posted at the running average cost price.
Before inventory close is performed these two transactions can still be marked to each other.
When a receipt transaction is marked to an issue transaction, the valuation method defined in the item's inventory model group will be disregarded and Microsoft Dynamics AX will settle these transactions to each other.
To mark an issue transaction to a receipt before the transaction is posted, open the form, select a transaction line, and then click the Inventorybutton on the transaction line and select Marking. The Markingform will open and display all the open receipt transactions. You can then select one of these transactions to match to, or mark, this issue transaction.
To mark an issue transaction to a receipt after the transaction has been posted, navigate to the inventory item on the Transactions on Itemform and click the Transactionbutton. Select the issue transaction that you want to mark, and then click the Inventorybutton and select Marking. The Markingform will open and display all the open receipt transactions. You can then select one of these transactions to match to, or mark, this issue transaction.
The following transactions are illustrated in the graphic below:
-
1a. Inventory physical receipt for a quantity of 1 at a cost of USD 10.00 each.
-
1b. Inventory financial receipt for a quantity of 1 at a cost of USD 10.00 each.
-
2a. Inventory physical receipt for a quantity of 1 at a cost of USD 20.00 each.
-
2b. Inventory financial receipt for a quantity of 1 at a cost of USD 20.00 each.
-
3a. Inventory physical receipt for a quantity of 1 at a cost of USD 25.00 each.
-
4a. Inventory physical receipt for a quantity of 1 at a cost of USD 30.00 each.
-
4b. Inventory financial receipt for a quantity of 1 at a cost of USD 30.00 each.
-
5a. Inventory physical issue for a quantity of 1 at a cost price of USD 21.25 each (running average of financial and physical updated transactions).
-
5b. Inventory financial issue for a quantity of 1 is marked to the inventory receipt 2b before the transaction is posted. This transaction is posted at a cost price of USD 20.00 each.
-
6a. Inventory physical issue for a quantity of 1 at a cost price of USD 21.25 each.
-
7 Inventory close is performed. Since the financially updated FIFO transaction is marked to an existing receipt, these transactions are settled to each other and no adjustment is made.
The new running average cost price reflects the average of the financially and physically updated transactions at USD 27.50.
The following diagram illustrates this series of transactions with the effects of choosing the FIFO inventory model with marking between issues and receipts.
Key to diagram
-
Inventory transactions are represented by vertical arrows.
-
Receipts into inventory are represented by vertical arrows above the timeline.
-
Issues out of inventory are represented by vertical arrows below the timeline.
-
Above (or below) each vertical arrow, the value of the inventory transaction is specified in the format Quantity@Unit price.
-
An inventory transaction value surrounded by brackets indicates that the inventory transaction is physically posted into inventory.
-
An inventory transaction value without brackets indicates that the inventory transaction is financially posted into inventory.
-
Each new receipt or issue transaction is designated with a new label.
-
Each vertical arrow is labeled with a sequential identifier, such as 1a. The identifiers indicate the sequence of inventory transaction postings in the timeline.
-
Inventory closings are represented by a red vertical dashed line and the label Inventory Close.
-
Settlements that are performed by inventory close are represented by dotted red arrows going diagonally from a receipt to an issue.