There are many ways that you can design and structure a workflow. The following sections provide examples of workflows and explain how documents move through each workflow.
 Workflow with
users
Workflow with
users
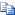
The following example illustrates a workflow with tasks and approval steps assigned to specific users.

To understand how a document moves through this workflow, assume that Sam has submitted an expense report totaling $7,000. In this scenario, Ivan must review the receipts that Sam routed to him, then Frank and Sue must approve the expense report.
After Sue approves the expense report, the workflow process ends.
 Workflow with
multiple users in an approval step
Workflow with
multiple users in an approval step
The following workflow example has an approval step that requires approval from more than one person. Notice that Sue, Jo, and Bill are the approvers in the second approval step.

When an approval step has multiple approvers, the action applied to the document is determined by the first person (or people) to respond.
You must select one of the following options when configuring an approval step with multiple approvers.
Single approver
If you select this option, the action applied to the document is determined by the first person who responds.
For example, assume that Sam has submitted an expense report for $15,000 and that it is currently assigned to Sue, Jo, and Bill. If Sue is the first person to respond to the document, the action she takes is applied to the document. For example, if Sue approves it, the document is sent to Ann for approval. If Sue rejects it, the document is rejected and sent back to Sam.
Majority of approvers
If you select this option, the action applied to the document is determined when a majority of approvers respond.
For example, consider the workflow previously illustrated. Assume that Sam has submitted an expense report for $15,000 and that it is currently assigned to Sue, Jo, and Bill. The first two approvers who respond—Sue and Jo—determine the action applied to the document.
-
If Sue approves the document and Jo rejects it, the document is rejected and sent back to Sam.
-
If Sue and Jo approve the document, the document is sent to Ann for approval.
Percentage of approvers
If you select this option, the action applied to the document is determined when a specific percentage of the approvers respond.
For example, consider the workflow previously illustrated. Assume that:
-
Sam has submitted an expense report for $15,000 and that it is currently assigned to Sue, Jo, and Bill.
-
You entered 50as the percentage.
In this scenario, the first two approvers who respond determine the action applied to the document. This is because the 50% requirement is met.
Assume that Sue and Jo are the first two approvers to respond.
-
If Sue approves the document and Jo rejects it, the document is rejected and sent back to Sam.
-
If Sue and Jo approve the document, the document is sent to Ann for approval.
All approvers
If you select this option, all of the approvers must approve the document in order for the workflow to continue.
For example, consider the workflow previously illustrated. Assume that Sam has submitted an expense report for $15,000 and that it is currently assigned to Sue, Jo, and Bill. If all of the approvers (Sue, Jo, and Bill) approve the document, it is sent to Ann for approval. If one person rejects the document, the document is rejected and sent back to Sam.
 Workflow with
multiple users in a task
Workflow with
multiple users in a task
The following workflow example has a task that is assigned to more than one person. Notice that Ivan, Kim, and Dean are assigned to the task.

A task can be assigned to multiple people; however, only one person can complete the task.
For example, assume that Sam has submitted an expense report totaling $7,000 and has routed his receipts to Kim. Kim must first acceptthe task. This indicates that she will complete the task. (The task is then removed from Ivan and Dean's work lists.)
Once Kim reviews the receipts, she marks the task as complete. The expense report is then assigned to Frank, and then to Sue, for approval.
After Sue approves the expense report, the workflow process ends.
 Workflow with
roles
Workflow with
roles
The following example illustrates a workflow with tasks and approval steps assigned to roles, or user groups.

To understand how a document moves through this workflow, assume that Sam has submitted an expense report totaling $7,000. In this scenario, a user in the AP Clerk role must review the receipts that Sam routed. Then Sam's manager and the controller must approve the expense report.
After the controller approves the expense report, the workflow process ends.
 Workflow with
a subworkflow process
Workflow with
a subworkflow process
The following example illustrates a workflow with a subworkflow process.

To understand how a document moves through this workflow, assume that Sam has submitted a purchase requisition totaling $7,000 for Adventure Works. In this scenario:
-
Ivan must review the line items on the purchase requisition.
-
Frank must approve the purchase requisition. (His approval is always required.)
-
Sue must approve the purchase requisition because it is greater than $5,000.
-
Amy must review the line items because the vendor is Adventure Works.
-
Mark must call the vendor because the vendor is Adventure Works.
-
Karl must approve the purchase requisition because the vendor is Adventure Works. After Karl approves the purchase requisition, the workflow process ends.
Now suppose that Sam has submitted a purchase requisition totaling $7,000 for Contoso, Ltd. In this scenario:
-
Ivan must review the line items on the purchase requisition.
-
Frank must approve the purchase requisition. (His approval is always required.)
-
Sue must approve the purchase requisition because it is greater than $5,000. After Sue approves the purchase requisition, the workflow process ends. The subworkflow tasks and approval steps are not required because the purchase requisition is for Contoso Ltd.